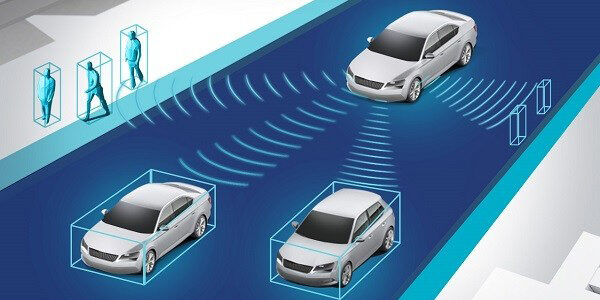
As the backbone of advanced autonomous driving systems, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is revolutionizing the automotive industry. This cutting-edge technology, which emits laser beams to detect and measure the position, speed, and other critical features of target objects, offers powerful information processing and sensing capabilities. Unlike traditional radar systems, LiDAR provides highly detailed environmental mapping, making it indispensable for the future of autonomous vehicles.
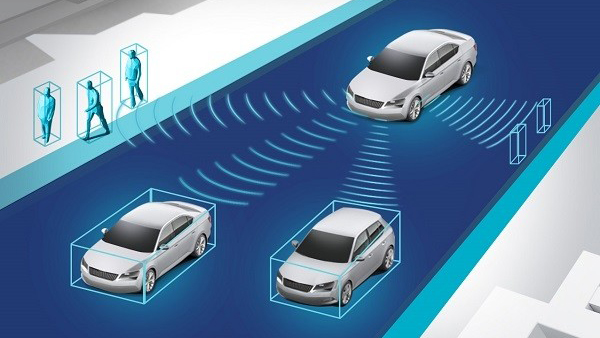
The Role of LiDAR in Autonomous Driving
In the automotive sector, LiDAR is becoming a cornerstone of autonomous driving technology. While currently integrated as part of advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), its potential extends far beyond, hinting at a pivotal role in fully autonomous vehicles. Typically, automotive LiDAR employs multi-beam designs, allowing vehicles to comprehensively perceive their surroundings, autonomously plan routes, and precisely control vehicle movements to achieve designated targets.

How LiDAR Works?
LiDAR functions by emitting laser beams that interact with objects in the environment. When these beams hit an obstacle, they reflect back to the sensor. By measuring the time delay between the emission and reception of the laser pulses, the system accurately calculates the distance to the obstacle. This capability enables vehicles to recognize intersections, navigate directionally, and identify critical environmental details essential for autonomous driving.
Differences Between LiDAR and Millimeter Wave Radar
While both LiDAR and millimeter wave radar are crucial in automotive radar systems, their operational principles and applications differ significantly.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging):
- Detection Mechanism: Uses laser beams.
- Wavelength: Much shorter, typically in the range of a few hundred nanometers.
- Data Output: Generates dense point cloud data that provides detailed 3D maps of the environment.
- Precision: High-resolution detection of objects, including their shape, size, and material.
- Application: Ideal for detailed environmental mapping and object recognition in autonomous driving systems.
Millimeter Wave Radar:
- Detection Mechanism: Utilizes millimeter waves.
- Wavelength: Significantly longer, within the millimeter range.
- Data Output: Provides basic shape and distance information about objects.
- Precision: Lower resolution compared to LiDAR, mainly detecting the general size and distance of objects.
- Application: Widely used in L1 and L2 level ADAS, such as adaptive cruise control.
Practical Applications and Integration
LiDAR‘s ability to gather extensive point cloud data and process it using artificial intelligence enables precise identification of obstacles such as humans, animals, vehicles, and trees. This intelligent recognition enhances the autonomous system’s ability to understand and respond to its environment accurately. In contrast, millimeter wave radar, although less precise, excels in cost-effective applications and is extensively utilized in current ADAS technologies for functions like automatic following.
Industry Examples and Future Prospects
Companies like Tesla are renowned for combining mature, cost-effective technologies with advanced software to achieve complex functionalities. Tesla’s current autonomous systems primarily rely on a combination of cameras and millimeter wave radar to provide real-time traffic information. However, as technology advances, LiDAR is expected to play a more central role in future autonomous vehicles, offering unparalleled precision and safety.
Summary
Automotive LiDAR and millimeter wave radar each have unique strengths and applications in autonomous driving. LiDAR offers high-resolution, detailed environmental mapping, making it essential for advanced autonomous systems. In contrast, millimeter wave radar provides cost-effective, reliable obstacle detection for current ADAS. As technology progresses, the integration of these systems will enhance the capabilities and safety of autonomous vehicles.
FAQ
Q: Why is LiDAR preferred over millimeter wave radar for high-precision autonomous driving?
A: LiDAR offers higher resolution and detailed 3D mapping capabilities, which are crucial for precise obstacle detection and environmental mapping. This level of detail is essential for the advanced decision-making required in autonomous driving.
Call to Action
CPJ Robot specializes in developing LiDAR and autonomous navigation robots. We offer customized solutions to meet your specific needs. For more information, visit our website and contact us today!