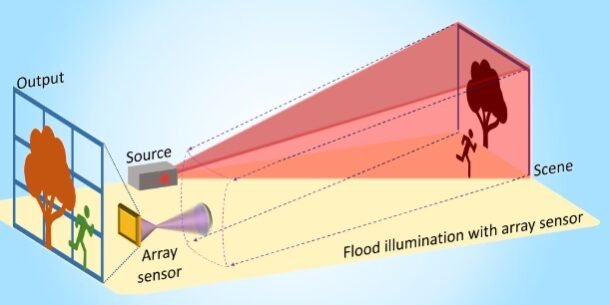
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology stands at the forefront of innovations driving the autonomous vehicle industry. As we delve into the intricacies of LiDAR, its principles, types, applications, and future challenges emerge as critical topics shaping the future of transportation technology.
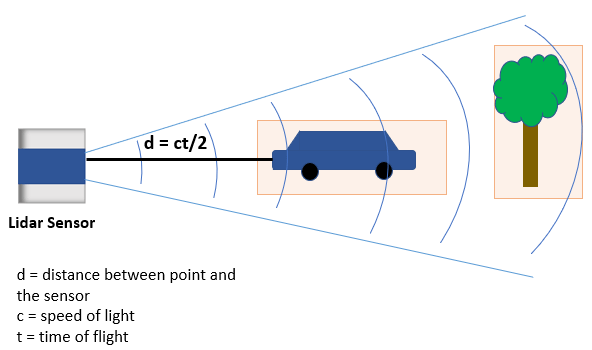
Principles of LiDAR Technology
At its core, LiDAR operates by emitting laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for these pulses to bounce back after hitting objects in the environment. This principle enables precise mapping of surroundings in three dimensions. A typical LiDAR system comprises a laser emitter, a receiver, and a scanning mechanism. The emitter sends out laser beams that bounce off objects and return to the receiver, which calculates distances based on the time taken for the laser pulses to return.
Types of LiDAR Systems
LiDAR systems can be classified based on their scanning methods: rotational LiDAR and solid-state LiDAR. Rotational LiDAR employs spinning mirrors or prisms to scan the surroundings, offering high-resolution 3D point clouds but at a higher cost due to mechanical complexity. On the other hand, solid-state LiDAR uses microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) or other solid-state technologies to achieve scanning without moving parts, promising lower cost and compact designs suitable for mass deployment in vehicles.
Applications in Autonomous Vehicles
The integration of LiDAR in autonomous vehicles is pivotal for several key applications:
- Obstacle Detection: LiDAR enables accurate detection of obstacles such as vehicles, pedestrians, and road signs, crucial for safe navigation in complex urban environments.
- Mapping and Localization: By generating detailed 3D maps of surroundings, LiDAR aids in precise localization of vehicles within their operational environment.
- Path Planning and Navigation: Autonomous vehicles rely on LiDAR data for real-time decision-making, ensuring efficient route planning and adaptive driving strategies.
Current Developments and Industry Trends
Recent advancements in LiDAR technology have spurred discussions on enhancing its capabilities:
- Cost Reduction: Historically, the high cost of LiDAR systems has been a barrier to widespread adoption. However, ongoing innovations in solid-state LiDAR promise significant cost reductions, making LiDAR-equipped vehicles more accessible.
- Performance Improvements: Newer LiDAR systems boast enhanced range, resolution, and reliability, catering to the demanding requirements of autonomous driving applications.
- Integration Challenges: Despite technological progress, challenges such as inclement weather conditions (e.g., rain, fog) affecting LiDAR performance remain areas of active research and development.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
Looking ahead, the future of LiDAR in autonomous vehicles faces several challenges:
- Environmental Variability: Adverse weather conditions and varying light intensities can impact LiDAR’s effectiveness, necessitating robust solutions to maintain operational reliability.
- Regulatory Considerations: Standardization and regulatory frameworks governing LiDAR use in autonomous vehicles are evolving, requiring alignment with safety and performance benchmarks.
- Technological Innovation: Continued advancements in sensor fusion, machine learning algorithms, and AI-driven perception systems will be pivotal in enhancing LiDAR’s role in autonomous vehicle ecosystems.
Explore CPJ Robot’s advancements in LiDAR technology and discover how they are shaping the future of autonomous driving. Visit CPJ Robot’s website for further information on their cutting-edge LiDAR solutions and contributions to the automotive industry.
In conclusion, LiDAR technology represents a cornerstone of autonomous driving innovation, offering unparalleled capabilities in environment perception and safety. As research and development efforts continue to evolve, LiDAR’s integration into mainstream automotive applications is poised to redefine the future of transportation, ensuring safer, more efficient, and sustainable mobility solutions globally.