Introduction
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology has made a significant impact in a variety of industries. Whether it’s used for self-driving cars or mapping terrains, LiDAR has become a critical tool for gathering accurate, real-time data. In this blog, we will explore 15 key applications of LiDAR, answering the essential questions: How is LiDAR used today? What sets it apart from other sensors? And why is POE LiDAR emerging as a game-changer?
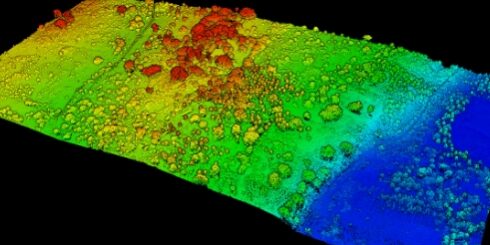
1. Topographic Mapping
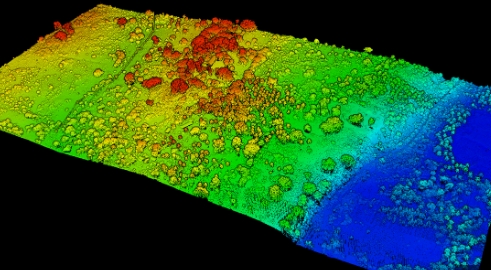
LiDAR excels in creating high-resolution maps by capturing minute elevation changes. This technology sends millions of laser pulses per second, making it an excellent tool for revealing terrain features. It has become the preferred method for accurate and rapid topographic surveys.
2. Construction Quality Control
LiDAR is invaluable in construction, ensuring structures adhere to Building Information Modeling (BIM) specifications. By comparing the point cloud from LiDAR scans with BIM designs, contractors can detect flaws early and avoid costly rework, saving time and money.
3. Bathymetric Surveying
While sonar has traditionally been used for underwater mapping, bathymetric LiDAR uses green wavelengths to penetrate water, enabling mapping down to the seabed. This technique is invaluable for both river and marine surveys.
4. Precision Agriculture
Farmers leverage LiDAR to optimize inputs like fertilizers in precision agriculture. By attaching LiDAR sensors to tractors, farmers can precisely measure biomass, crop height, and volume, reducing waste and increasing yield.
5. Forest Mapping
LiDAR helps visualize tree height and forest structure, even in dense canopies. By capturing light that filters through tree gaps, LiDAR provides a true vertical profile of forests, allowing accurate 3D vegetation models.
6. Autonomous Vehicles
LiDAR plays a crucial role in self-driving cars. The 360-degree LiDAR sensors mounted on vehicles continuously scan the surroundings, helping cars identify obstacles and make real-time decisions, enhancing safety.
7. Flood Risk Mapping
Hydrologists use LiDAR to create digital elevation models (DEMs) that predict flood-prone areas. By analyzing surface topography, LiDAR helps in the development of early flood warning systems, crucial for disaster preparedness.
8. Land Use Planning
LiDAR can classify terrain into categories such as vegetation, buildings, and roads based on reflected pulses. By monitoring changes over time, it assists in land-use planning and monitoring environmental changes.
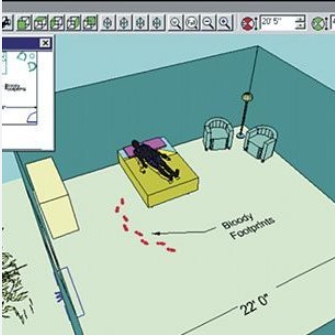
9. Crime Scene Reconstruction
LiDAR has become a vital tool in forensic investigations, helping law enforcement recreate accident and crime scenes. By scanning the scene, LiDAR enables the accurate reconstruction of events for further analysis.
10. Slope Monitoring
For landslide risk assessments, LiDAR accurately maps surface features in vegetated areas. Geologists can analyze slopes, create risk maps, and predict potential landslide areas, enhancing public safety.
11. Atmospheric Monitoring
LiDAR has several atmospheric applications, including:
- Doppler LiDAR: Measures wind speed.
- Raman LiDAR: Tracks water vapor and aerosols.
- Differential Absorption LiDAR (DIAL): Measures ozone and water vapor, providing crucial data for environmental monitoring.
12. Asset Management
Mobile LiDAR is used in cities to monitor infrastructure like roads, bridges, and utility lines. The data is processed and stored in GIS databases, allowing for effective asset management and ensuring safety standards.
13. Ice and Snow Mapping
LiDAR helps measure snow depth in polar regions, providing essential data for hydrology and avalanche forecasting. As LiDAR modeling improves, it becomes an even more valuable tool in understanding frozen landscapes.
14. Augmented Reality (AR)
With the integration of LiDAR sensors into smartphones, augmented reality (AR) applications are taking off. LiDAR adds depth-sensing capabilities to enhance gaming and practical applications such as site planning for utilities like solar panels and wind turbines.
15. Power Line Inspection
LiDAR detects vegetation encroachment on power lines, a common cause of outages. Its dense point cloud data helps utility companies manage vegetation risks, preventing trees from interfering with overhead power lines.
Conclusion
LiDAR technology continues to grow and find new applications across various sectors. Whether it’s improving autonomous driving safety, enhancing AR experiences, or assisting in environmental monitoring, LiDAR’s versatility makes it a valuable tool. POE LiDAR, in particular, offers benefits such as simplified installation and accurate real-time data collection, making it ideal for applications that demand precision and efficiency.
By following this comprehensive guide, you’ll gain a better understanding of LiDAR’s widespread applications and how POE LiDAR is making it easier to implement this technology across various industries.
FAQs:
- What is POE LiDAR, and how does it differ from traditional LiDAR? POE LiDAR combines Power over Ethernet with LiDAR sensing, simplifying installation and reducing wiring complexity.
- How is LiDAR different from other sensors like radar or sonar? While radar uses radio waves and sonar uses sound waves, LiDAR uses laser light, providing higher precision and resolution.
- What industries benefit the most from LiDAR technology? LiDAR is widely used in sectors like construction, agriculture, autonomous vehicles, and environmental monitoring.